Chagrin Falls Veterinary Center & Pet Clinic with Dr. Carol Osborne. Located in Chagrin Falls, Ohio at 530 East Washington Street. Chagrin Falls Veterinary Center & Pet Clinic is operated by Veterinarian & Pet Celebrity Dr. Carol Osborne, the Integrative Pet Wellness Center offers traditional & natural alternative pet health products & therapies for dogs & cats.
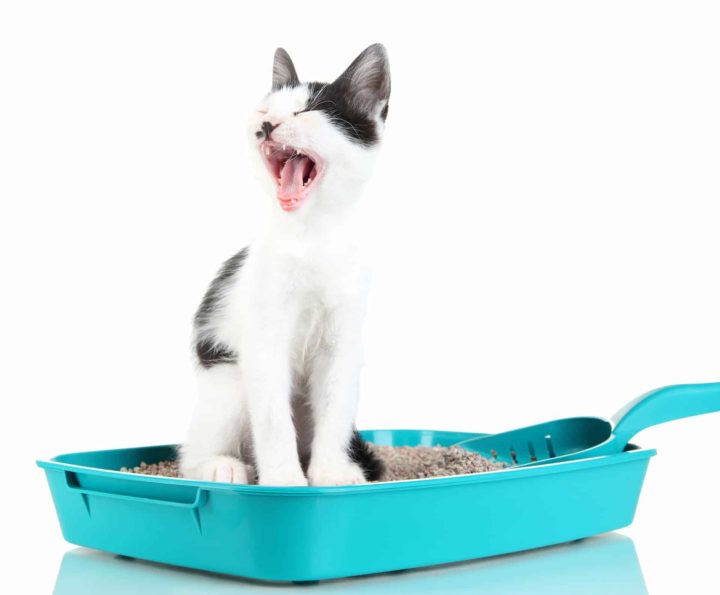
Failing to use the litter box is the number one behavioral problem cat owner’s face. It is also a leading cause of euthanasia. All medical and psychological causes must be ruled out by your vet before this diagnosis can be confirmed.
Proper play promotes socialization and a well-socialized kitten makes a great pet. Begin to socialize your kitten as soon as you bring him or her home, ideally at eight weeks of age. That’s the best time for kittens to bond with people.
Cat Diseases
Feline Leukemia is the leading viral killer of cats today. The virus is spread by prolonged cat-to-cat contact and through bite wounds. The virus is shed in saliva, tears, urine, and feces.
Feline Blood Loss/Anemia results from a low number of red blood cells in the circulation. Red blood cells normally carry oxygen and vital nutrients to all tissues of the body.
Feline Heart Problems
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most common heart disease in cats affecting heart muscle function so that it can not pump blood effectively. Blood circulation is impaired and the body is deprived of oxygen and vital nutrients.
Feline Urinary Tract Problems
Urine forms in the kidneys, is stored in the urinary bladder, then passes through a narrow tube called the urethra, and is eliminated. Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease – (FLUTD) is a common group of conditions affecting the urinary bladder and/or urethra in neutered cats.
Feline Kidney Problems
The kidneys filter and remove toxic waste products from the cat’s blood via the urine. They also regulate calcium and vitamin D levels, maintain the cat’s level of hydration and secrete the hormone responsible for red blood cell production.
Cat Liver Problems
The liver is a vital organ and is affected by 5 major disorders in cats. These include toxins from poisons or bacteria; a variety of Cancers which tend to spread and Portosystemic Shunts in which blood circulation in the liver is abnormal.
Hormone Disorders in Cats
The hormone or endocrine system is made up of seven glands that produce substances called hormones, which travel to different parts of the body and stimulate a response. Disorders occur when the glands produce either too much or too little of a particular hormone.
Your Cat’s Golden Years
Over 75% of our cats and dogs have passed middle age and are entering their “golden years”.
To call a cat old, one mustn’t consider chronological age, but rather physiological condition. Biological and chronological aging are not inexorably linked.
Systemic Illness
Systemic illness is defined as a disease of any major organ system or any condition that ultimately affects the whole body. The signs will vary depending on which organ system is involved, for instance the heart, liver or kidneys.
Feline Hair Loss
Alopecia is defined as the absence of hair from areas that are normally hairy. Hair loss may involve thinning of the hair or complete hair loss. Itching may or may not be a factor.
Cat Abscesses
An abscess is a pocket of pus under the skin. Pus is an accumulation of bacteria and white blood cells and indicates the presence of infection. The problem is detection because cat fur is so dense an abscess is easy to miss initially.
Cat Claws
Cats use their claws to climb, scratch, defend themselves, and hunt outside. They also use them to “mark” their territory, which is instinctive behavior. Provide a scratching post from day one and give your cat clear messages about which objects she may or may not scratch.
Bees, wasp, spiders, centipedes and other flying insects bite and sting cats. Most bites occur on the face which swells and is painful. Occasionally the paws are affected. Most bites go unnoticed and heal on their own.
Stud tail is actually Seborrhea of the tail. Cats have 2 types of skin glands. Sweat glands, most of which are non functional and sebaceous glands. Sebaceous glands are associated with hair follicles and produce an oily substance called sebum.
Excessive exposure to the sun can cause a skin condition called Solar Dermatitis. This is primarily a problem in breeds with sparse fur like the Sphynx. Skin areas that are lightly pigmented and cats with white skin are also at risk. The ear flaps are the most common site affected.
Feline acne is a skin condition affecting the cats chin. Overactive oil (sebaceous) glands in the chin produce excess oil or sebum which predisposes cats to developing Feline Acne and Stud Tail. The oil, which is also called Sebum, plugs up the hair follicles in the chin which causes black heads called Comedomes to form.…
Lice are tiny, six-legged parasites that feed on blood and can cause anemia. Weak, run-down kittens are most susceptible. Tiny white spots, called nits are visible. These are the egg casings. Lice spend their entire life on the animal and are not transferable to other pets or people. They do not infest your home and…
Dry skin is common, especially when the weather gets cold and we have to turn the heat up indoors. Dry skin is flaky and often has white scales that resemble dandruff. Diets deficient in essential omega-3 fatty acids and zinc can lead to dry skin, as can bathing your cat with the wrong shampoo or…
External parasites bothersome to cats include fleas, ear mites, mange mites and walking dandruff mites. Notoedric mange is also called Feline Scabies and is caused by a microscopic mange mite called Notoedres cati. Notoedres mites in cats are similar to Sarcoptic mange mites in dogs. Notoedric mange causes intense itching. Lesions begin on the ear…
Heartworm disease is a serious and potentially fatal disease caused by worms called Dirofilaria immitus. These worms are “spaghetti-like”, grow up to 12″ long, and reside in the heart. The Larval Form of this worm is transmitted by the bite of a mosquito. Cats of all ages and breeds are susceptible but three to six…
Itching is the most common sign of allergies in cats and dogs. Allergic dermatitis is inflammation of the skin that occurs after it has been exposed to something to which it is allergic, known as an allergen. The number-one sign of allergies in pets is itching. Cats lick, bite, chew and scratch themselves to the…
Prepare everything in advance: use a figure-8 harness attached to a leash that can be fastened to the wall next to your tub or sink with a suction cup. This will secure the cat and leave both your hands free. BATHING YOUR CAT Place a non-skid rubber mat on the bottom of the tub or…
Regular grooming helps keep your cat’s skin and haircoat in good health. It decreases hairballs and mats, removes dead skin and hair, and degreases the coat. Grooming also gives you a chance to check for fleas and ticks, as well as lumps and bumps. A quality diet that supplies the essential vitamins and minerals helps…
Skin diseases are very common in cats. They can occur because of bacterial, viral, fungal, allergic, parasitic, and hormonal disorders. In older cats, skin cancer and cysts are not uncommon. Signs of skin problems are among the easiest to detect. They include dry flaky skin, as well as red, raw irritated areas often with hair…
Food allergy is an abnormal or a hypersensitive reaction to a food ingredient which is usually a protein. 10-20% of allergies in cats are caused by food. CAUSES Beef, dairy products and fish, especially tuna and mackerel are responsible for almost 90 percent of food allergies in cats. These products cause a skin reaction as…
Constipation is the infrequent passage of stool and/or straining to defecate. The feces may be hard or just firmer than normal. Recurrent constipation can lead to Obstipation which is the term used for severe, persistent constipation. The colon, which is the end or terminal portion of the large intestine, becomes dilated and enlarged. Stool retained…
Diarrhea is defined as a change in the frequency, consistency or volume of stools. It is the most common sign of disease of the small intestine in cats and dogs. Abnormal intestinal absorption of nutrients is usually the underlying cause which can occur because of a variety of infectious, toxins and/or dietary factors. SYMPTOMS * Large volumes of…
How Much Playtime Do Cats Need? Cats needs at least 10-15 minutes of exercise three to four times a day. The exact amount varies with age, breed, health and physical condition. Indoor cats need to play 3 to 4 times as much as outdoor cats to satisfy their needs for exercise. One hour of playful…